During a seizure, there are bursts of electrical activity in your brain, sort of like an electrical storm. This activity causes different symptoms depending on the type of seizure and what part of the brain is involved.

Evidence-based guideline: Management of an unprovoked first seizure in adults Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Epilepsy Society
Mar 10, 2011 · Learn about epilepsy, or seizure disorder. Causes include head injury, trauma, prenatal injury, poisoning, medications, stroke, heart attacks, alcoholism, infection, and more.
11.00 Neurological. A. Which neurological disorders do we evaluate under these listings? We evaluate epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, coma or persistent vegetative state (PVS), and neurological disorders that cause disorganization of motor function, bulbar and neuromuscular dysfunction, communication impairment, or a …
Epilepsy is a chronic condition characterized by recurrent seizures. Seizure definition, phases, and types are described in this intro to complete section on epilepsy …

Why Does My Have Seizures?. Written by: Roy Dvorak. A may seizure for any number of reasons. Just because a has a seizure …
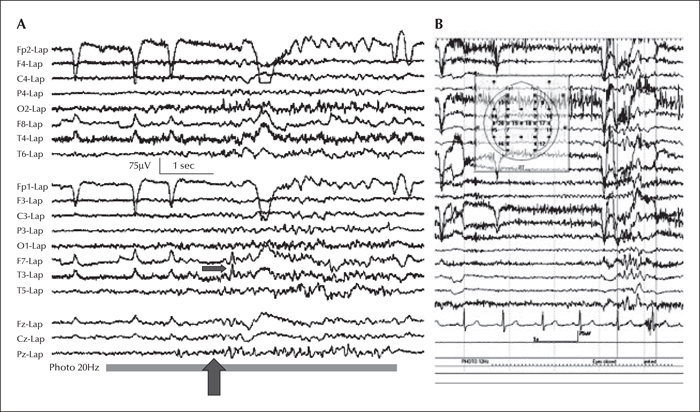
Observing Seizures [scald=3901:sdl_editor_representation] What to observe before, during and after seizures [scald=5181:sdl_editor_representation] Describing seizures with …




Seizure – an easy to understand guide covering causes, diagnosis, symptoms, treatment and prevention plus additional in depth medical information.
Observing Seizures [scald=3901:sdl_editor_representation] What to observe before, during and after seizures [scald=5181:sdl_editor_representation] Describing seizures with …

Epilepsy is a chronic condition characterized by recurrent seizures. Seizure definition, phases, and types are described in this intro to complete section on epilepsy …
